Chapter 3: Increase High Quality Protein
Chapter 3: Increase High Quality Protein
What does it mean to increase quality protein?
It means making protein a priority in every meal—and choosing high-quality sources that are rich in nutrients, easy to digest, and low in additives or processed fillers.
Protein is more than just “meat.” It’s a powerful blood sugar stabilizer. It helps keep you full, supports your muscles, and slows down how fast sugar is absorbed into your blood when you eat carbs.
When you pair carbs with protein, the sugar from those carbs gets absorbed more gradually—which is exactly what we want.
Protein is necessary to heal and recover from injuries, and also to build and maintain muscle when doing exercises to increase strength. The increased muscles will also improve your metabolism as well as your insulin sensitivity.
Where can you find quality protein?
Quality protein can be found in both animal and plant sources. The key is to focus on lean, whole, minimally processed options.
Animal-based proteins:
🐔 Chicken breast, 🦃 turkey
🐟 Fish (especially fatty fish like salmon, sardines, mackerel)
🥚 Eggs
🥛 Greek yogurt (unsweetened), 🧀 cottage cheese
🍖 Lean beef or lamb (in moderation)
Plant-based proteins:
🫛 Lentils, chickpeas, black beans
🌱 Tofu, tempeh
🌰 Nuts and seeds
🥜 Natural peanut or almond butter (no added sugar)
🌿 Plant-based protein powders (unsweetened)
If you’re on a budget or don’t have time to cook, hard-boiled eggs, plain Greek yogurt, or canned tuna are quick wins.
When should you increase protein intake?
📌 At every meal.
Ideally, every time you eat, you should ask: Where’s the protein?
Especially important:
🥞 Breakfast – some people eat only carbs in the morning, which causes a blood sugar spike and crash
🧃 When snacking – avoid sugary or carb-heavy snacks, choose protein instead
💪 After exercise – helps repair muscles and balance blood sugar
🍽️ Before high-carb meals – protein first, carbs later
This helps control your appetite, support metabolism, and improve insulin sensitivity.
Why is protein so important for blood sugar control?
Because protein is digested more slowly than carbs. That means:
🧘 It slows sugar absorption
💪 It builds and preserves muscle, which improves insulin function and blood sugar utilization.
🧠 It helps reduce sugar cravings and keeps you full longer
🔄 It helps regulate sugar when paired with fats and fibre
⛔ And it doesn’t spike blood sugar on its own!
Studies show that eating protein with meals helps reduce post-meal blood sugar spikes—especially when it’s eaten before the carbs.
How do you increase protein practically and enjoyably?
Here are some easy and enjoyable ways:
✅ Start your day with eggs or a protein smoothie instead of sugary cereal or bread
✅ Add grilled chicken, boiled eggs, or beans to salads
✅ Snack on nuts, seeds, or Greek yogurt
✅ Try tuna lettuce wraps or stir-fry tofu or tempeh
✅ Use protein powder in smoothies, pancakes, or even coffee
✅ Mix protein with fiber and healthy fats for the best blood sugar control
Don’t wait until dinner to get your protein—spread it out throughout the day.
🍽️ Simple Blood Sugar-Friendly Recipe
🐟 Delicious Salmon Salad Bowl
Ingredients (Serves 1):
250 grams of salmon fillet
½ cup of baby spinach
¼ cup of chopped celery and red onion
1 tsp of lemon juice
1 tbsp olive oil
Salt & pepper for seasoning
Sprinkle of chili flakes or herbs (optional)
Instructions:
Cook salmon to your preference.
In a bowl, add salmon, baby spinach, celery and red onion.
Drizzle olive oil, lemon juice on top and season with salt, pepper, herbs or spices.
Nutritional Info (approx.):
Calories: 420 kcal
Protein: 38g
Carbs: 5g (mostly from celery, red onion, and spinach)
Fats: 27g (healthy fats from salmon & olive oil)
Fiber: 2g
Sugar: <2g
Key nutrients: Omega-3, Vitamin D, B12, Niacin, B6, Vitamin K, Vitamin A, Folate,
Benefits:
✅ Protein-rich
✅ Full of fiber
✅ Keeps you full and energized
✅ Stabilizes blood sugar for hours
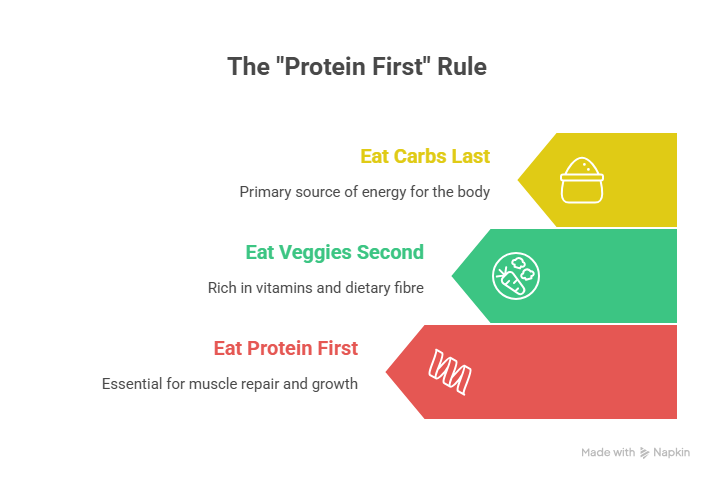
👀 Visual Tip: The “Protein First” Rule
Whenever you sit down to eat, follow this order:
🥚 Step 1 – Eat the Protein
🥗 Step 2 – Eat the Veggies (fibre)
🍚 Step 3 – Eat the Carbs (if any)
This simple change can reduce your post-meal blood sugar spikes by up to 30–50% (according to multiple studies!).